Retirement is an important turning point in life and the National Pension System must be with you. Every person has plans after retirement, how they want to spend their retirement life. Wanting to go on trips, pursue their hobbies which they missed and many things which they kept aside during their working life. Everyone will retire one day and your paycheck will stop, but still, you need money because life is not over, your plans have just started. After “Plan 1 – build the emergency fund” let’s discuss Plan No. 2 to make provisions for our after-retirement life.
Disclaimer: Investments in the securities market are subject to market risks, read all the related documents carefully before investing. This content is purely for information purpose only and in no way to be considered as an advice or recommendation.
What is the National Pension System?
After retirement, you will not receive a salary in your bank account. It will be scary like continuing work even in your old age if you do not plan retirement in your early days or do not start the proper investment at the right time. These days, many government-backed and non-government-backed pension and retirement plans are available in the market. This blog will go through one of the most popular government-backed initiatives “National Pension Systems”.
December 22, 2003, established a pension system called the “Contributory Pension System” later renamed “National Pension System”. Initially, it was designed for newly joined employees in the centre government job on or after January 1, 2004. Later, the government decided to extend benefits and retirement safety life to citizens of Bharat. They want every citizen to have a peaceful retirement life, for that, people must invest in pension-focused schemes. So the government allowed individuals to participate in the NPS. NPS provide retirement income security to Bhartiya. It is government-sponsored and regulated by the Pension Fund Regulatory and Development Authority ( PFRDA ). The government kept the fund management charges cheap, making it one of the cheapest actively managed funds.
How many types of accounts are available ?
The NPS scheme has two account types. Tire I and Tire II accounts.
Tier I Account:
This is the primary account and is mandatory for subscribers. The main object of this account is to create a retirement corpus. Disciplined, regular contributions and better appreciation generate a good corpus. The minimum investment is 500 Rs and 1000 Rs contribution per year. Any individual between the age group of 18 to 70, whether he/she is an employee of the private sector or government, a small businessman or anyone can open an account in NPS. Non-resident or Overseas Citizens of India can also open an account.
Tier II Account:
A Tier II is a voluntary account, linked to a Tier I account. You must have an active Tier I account to open an account. The minimum opening amount is 1000 Rs and the minimum contribution is 250 Rs. A Tier II account is not as strict as a Tier I on withdrawal, you can generally withdraw any amount, anytime and can also transfer to a Tier I account. It acts like a savings account.
Withdrawal Restriction:
A Tier I account is a pension account whose primary responsibility is to generate a retirement corpus. That is why regulators imposed stricter regulations and withdrawal limitations. The fund is locked until retirement or the age limit (60 Years). Life is unpredictable and sometimes we need money to fulfil present-day requirements, so the government allowed some early partial withdrawals after 3 years from the opening date. You can withdraw up to 25% amount of your contributions.
These partial withdrawals are allowed under specific conditions like higher education, marriage, construction or purchase of a home or medical treatment of critical illness. Of course, this is contingent upon providing sufficient documents. During the total investment period, subscribers are allowed only 3 withdrawals and the gap between withdrawals must be 5 years.
Sometimes subscribers decide to pre-mature exit, then 80% of the corpus is used for the annuity plan but if the total corpus is less than or equal to 2.5 lakh, the subscriber can withdraw the entire amount from the account.
On retirement, you will receive a lump sum of 60% of your corpus. It is completely Tax-Free. The remaining 40% of the corpus will be used to purchase an annuity plan. The amount received from an annuity plan will be treated as taxable income. If the corpus is less than or equivalent to 5 lakh then Subscribers can withdraw the entire amount from an account.
Annuity Purchases: :
Annuity purchase is mandatory in the National Pension System. 40% of the corpus will be used to buy a financial product called an annuity plan. An annuity plan is like an insurance product. It ensures you receive some amount throughout your retirement years. Conversely, you will have limited access to your principal amount. Overall, annuity purchases in NPS ensure guaranteed income for your post-retirement life. You enjoy peace of mind, knowing you have a reliable income source of money to take care of expenses.
Tax Benefits:
The purpose of NPS is financial security for life after retirement, it is a necessity of every citizen. So the government gives TAX benefits to bring more people on board and motivate them to contribute towards their own retirement life. Pension schemes save TAX money that subscribers can use for different purposes. NPS are eligible for tax benefits under sections 80CCD(1) and 80CCD(1B) of the Income Tax Act. This means you can claim 1.50 lakhs under Sec 80CCD(1) ( This deduction is included within the overall Section 80C limits of 1.5 lakh ) and an additional 50,000 under Sec 80CCD(1B).
Under the 80CCD(1) section, the maximum deduction allowed is up to 10% of the salary ( Basic + DA ) of the individual employee. This deduction is subject to an overall ceiling of 1.5 lahks under
Section 80CCE includes other deductions like EPF and Life Insurance Premium. Etc. Both sections 80CCD(1) and 80CCD(1B) deductions are available only for contributions made to own account and not for someone else’s account e.g. Wife or child do not qualify for these deductions.
Where does our money get invested?
So now the biggest question arrives, where does the National Pension System invest subscriber’s money? It is a market-linked scheme and subscribers have different asset categories in which they can distribute money. Subscribers can invest in the following categories.
- Asset Class E: Equity
- Asset Class G: Government instruments.
- Asset Class C: Corporate instruments.
- Asset Class A: Alternative investments Funds and instruments like REITS. CMBS etc.
To invest and manage fund subscribers choose Pension Fund Manager ( PFM ) and investment method i.e. Auto or Active method. The list of funds that offer Fund Managers ( available on 1 May 2024 ).
- Birla Sunlife Pension Management Limited
- HDFC Pension Management Company Limited
- ICICI Prudential Pension Funds Management Company Limited
- Kotak Mahindra Pension Fund Limited
- LIC Pension Fund Limited
- Reliance Capital Pension Fund Limited
- SBI Pension Funds Private Limited
- UTI Retirement Solutions Limited
Subscribers have the option to change pension Fund Manager if unhappy with the performance. After appointing a Pension Fund Manager, you can choose investment options, Active or Auto investment. Let’s check and understand how they work and choose the correct one at your convenience.
Investment allocation, Fund Manager information and other information are registered with the Central Record-Keeping Agency ( CRA ). CRA maintains records of contributions and investments, operations of accounts, etc. In short CRA act as coordinator or communicator between Subscribers and Pension Fund Manager.
If subscribers want to manage their investments, the Active option is the most appropriate for such people. In the active option, subscribers can distribute corpus in the 4 assets category according to their choice. Subscribers can manage risk and growth.
There are some rules for allocations. The total allocation across E, C, G and A asset classes must be equal to 100%. Up to 50 years of age, subscribers can allocate maximum allocations i.e. 75% of corpus to Equity asset class but after 51 years of age, it will start to reduce to manage risk. The below table will help you to understand.
| Age ( Years ) | Maximum Equity Allocations |
| Up to 50 | 75% |
| 51 | 72.50% |
| 52 | 70% |
| 53 | 67.50% |
| 54 | 65% |
| 55 | 62.50% |
| 56 | 60% |
| 57 | 57.50% |
| 58 | 55 |
| 59 | 52.50% |
| 60 and Above | 50 |
Auto Options
If you do not have proper investment knowledge, about the equity market and its risk then the Auto option is the best choice. The auto option changes your allocation according to age and risk-taking capabilities. It is like the life cycle fund because the invested corpus in assets will change according to the subscriber’s age. All these features make it a pre-defined portfolio. As age increases, exposure to equity and corporate debts is managed accordingly.
There are 3 options under ‘Auto Choice’ depending on the risk-taking capacities of subscribers.
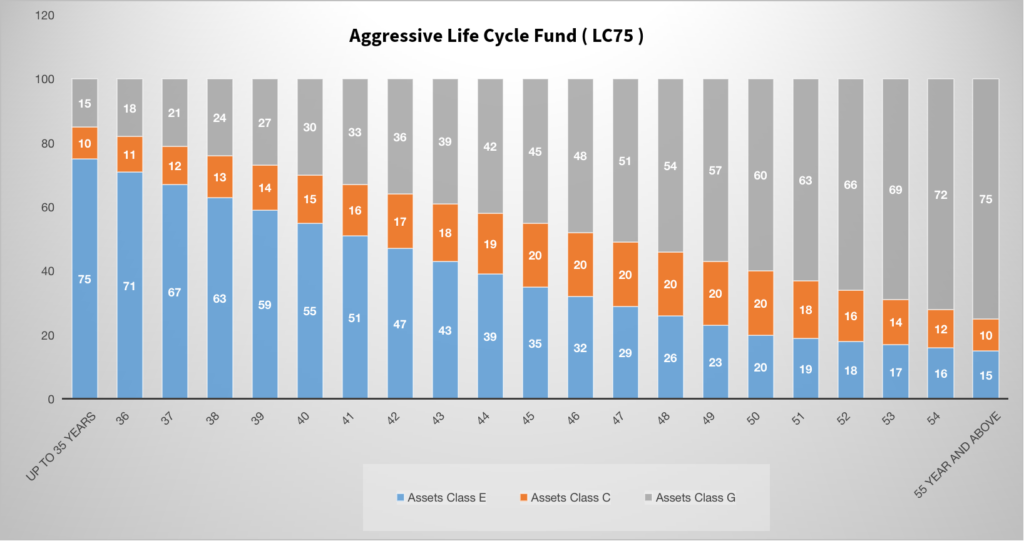
Aggressive Life Cycle Fund ( LC75 )
In this option, 75% of the corpus will be invested in Equity assets and from age 36 it starts to reduce as per the age of subscribers. At a young age, subscribers can take risks for better returns.
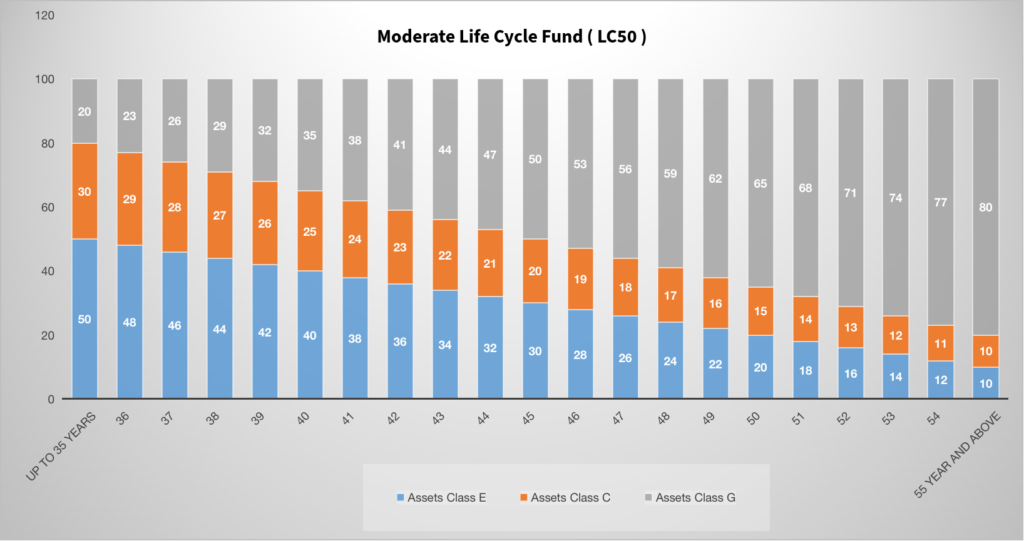
Moderate Life Cycle Fund ( LC50 )
In this option, the fund allows 50% of the corpus to be invested in Equity assets till 35 years of age and starts to reduce as per the age of subscribers. In this option, subscribers can have more balance between risks and growth.
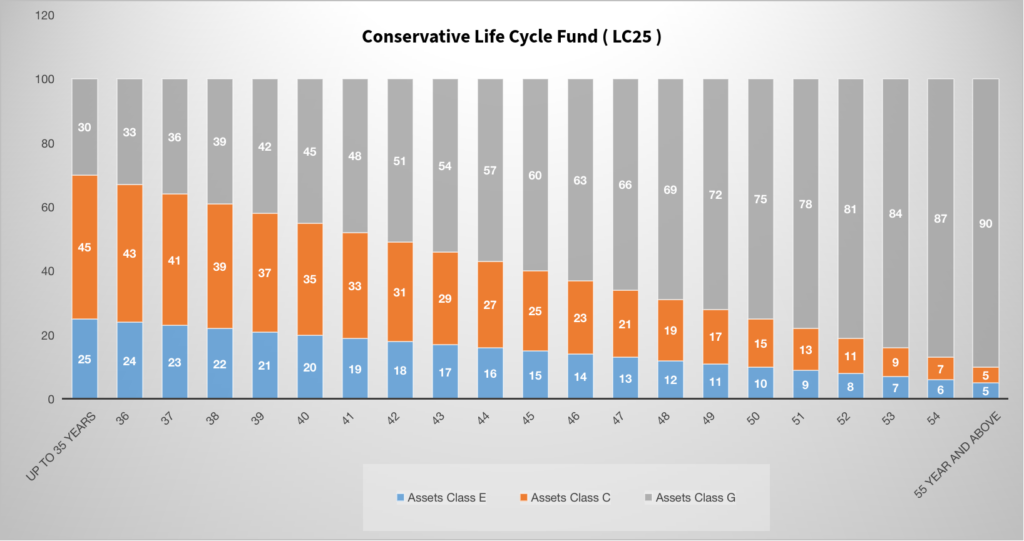
Conservative Life Cycle Fund ( LC25 )
In this option, the maximum allocation of the corpus is to Corporate and Government assets. This fund keeps a cap of 25% of the corpus in Equity Assets and reduces it according to age on the other side allocation to the Government debt asset increased which is considered the most secure asset to invest.
Important Links
- Calculate your pension with the “Pension Calculator“.
- Read Investor Charter
- Open an Offline / Online NPS Account
Disclaimer: Investments in the securities market are subject to market risks, read all the related documents carefully before investing. This content is purely for information purpose only and in no way to be considered as an advice or recommendation.


